80EEA deduction for income tax on home loans| In India, the provision of 80EEA helps first-time home buyers with an additional relaxation facility at the Department of Income Tax. As per Section 80 of the EEA Income Tax Act, any first-time home buyer in India can get an additional tax deduction of up to Rs. 1.5 lakhs Buying a property that is affordable and needs to be backed by a mortgage loan, buyers can get benefits and deductions in two departments viz. Deductions 80EE and 80EEA. In this article, we will only discuss Section 80EEA of the income tax law.
In the year 2014, the flagship project named Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY) was launched with the mission of 'Housing for All by 2022'. This was one of several initiatives undertaken to encourage people to own their property. To further support such initiatives, the 80EEA deduction was introduced in 2019. Through this, the government extended its support to home loans applied between April 1, 2019, and March 31, 2021; eventually this was extended until March 31, 2022.
With Section 80EEA, more and more people were able to fulfill their dream of having their own homes.
What is Section 80EEA?
In India, a single first-time home buyer can enjoy a deduction of up to Rs. 1.50 lakh under Section 80EEA if they buy an 'affordable property. This deduction is on top of the initial deduction and the basic deduction under Section 24(b).
Thus, the total annual tax refund is close to Rs. 3.5 lakhs. By purchasing the property, the buyer cannot own any other property. Since the deductions only apply to 'affordable property, we first need to understand what an affordable property is.
What is affordable home ownership?
Income tax law 80EEA came into effect on 1st September 2019. Prior to that, "acquirable property" as those worth only up to 50 lakhs. With the implementation of Section 80 EEA, in the income tax law, the new definition will become "affordable house" property worth up to Rs 45 lakhs. The carpet area of the house also affects the affordability of the house.
No property in the urban city must exceed 60 square meters or 645 square feet to be eligible for the Section 80EEA deduction. In the case of real estate in other cities that do not exceed 90 square meters or 968 square feet that are under the benefits of the same Department.
What are the conditions to claim the benefit?
Various conditions have been applied to claim tax relief under Section 80IA of the Income Tax Act. They are as follows—
To purchase residential home ownership, a loan must be obtained from a housing finance company or financial institution.
The individual cannot be a claimant of the deduction that comes with Section 80EE.
Stamp duty for the residential property must be 45 lakhs or less.
This must be the buyer's first purchase. If you have a house registered in his name, you will be notified whether or not you are eligible for the article 80 LEE deduction.
The date to claim the home loan must be between April 1, 2019, and March 31, 2021.
In metropolitan cities, the carpet area of the residential property must be greater than 645 square feet or 60 meters.
In other cities, the carpet area of the residential lot may not exceed 968 square feet or 90 meters.
What is the amount of the deduction?
As per the Income Tax Act, Section 80 EEA, an exemption on the principal amount of up to Rs. 1,50,000 is available. This is eligible for over Rs. 2 lakh available under Section 24(b). Therefore, a taxpayer can enjoy a full deduction of Rs. 3.5 lakh who meet all the eligibility criteria included in Section 80 of the EEA Income Tax Act.
What is the limit under Section 80EEA?
If the borrower of a mortgage loan has availed himself of the deduction under section 80EE, he cannot claim the deduction under section 80EE.
Can co-owners claim the deductions included in Section 80EEA?
In the case of co-owners or co-borrowers, each of them is eligible to claim a deduction of Rs. 1.5 Lakh under Section 80 LEE. However, each must meet all the criteria.
Difference between 80EEA and Section 24
80EEE and Section 24: both sections are involved in claiming the deduction. However, there are some fundamental differences that need to be noted in this regard.
In the case of a section 80EEA deduction, possession is not required; once you start the interest payment process, you can claim an exception. However, in the case of Section 24, you must own the property to claim the deduction.
Under 80EEA, one can choose mortgage loans only from different banks and financial institutions. However, in the case of section 24, Loans can also be obtained from friends and family; who is also allowed for exceptions as long as all documents are correct.
The main difference between the two is the monetary amount involved. For 80 EEA, the deduction is 1,50000, but for 24 A, the deduction can be claimed in the amount of up to 2,00000 Lakhs.
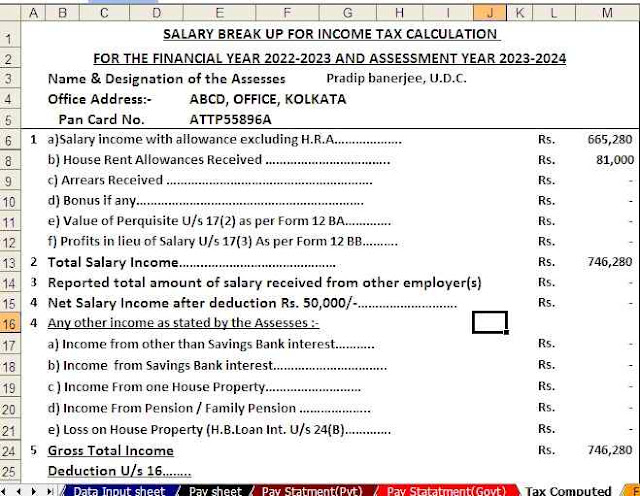
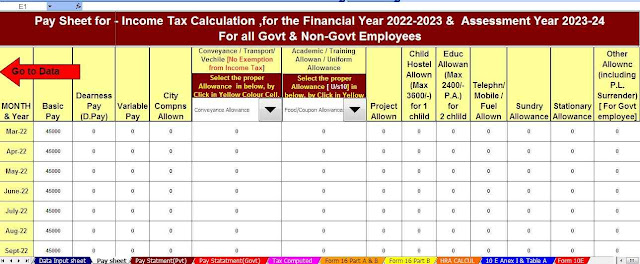
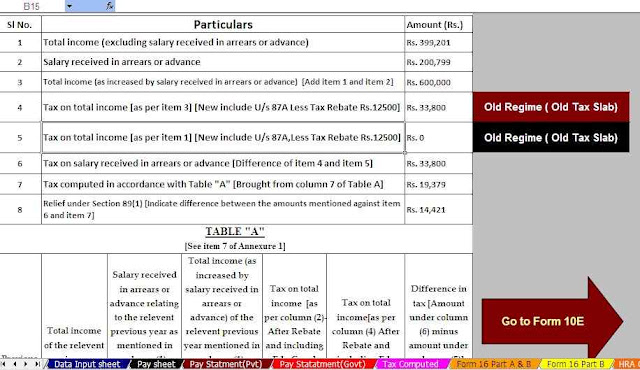
Feature of this Excel Utility:-
1) This Excel utility prepares and calculates your income tax as per the New Section 115 BAC (New and Old Tax Regime)
2) This Excel Utility has an option where you can choose your option as New or Old Tax Regime
3) This Excel Utility has a unique Salary Structure for Government and Non-Government Employee’s Salary Structure.
4) Automated Income Tax Arrears Relief Calculator U/s 89(1) with Form 10E from the F.Y.2000-01 to F.Y.2022-23 (Update Version)
5) Automated Income Tax Revised Form 16 Part A&B for the F.Y.2022-23
6) Automated Income Tax Revised Form 16 Part B for the F.Y.2022-23


0 Comments